BECE 2022 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The energy transformation that takes place in a solar cell is
Solution: Solar cells convert light energy directly into electrical energy.
2. All flowering plants end their life cycle with
Solution: Seed formation marks the end of a flowering plant's life cycle.
3. Soil texture is a term used to describe the
Solution: Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
4. Which of the following processes is an example of a physical change?
Solution: Magnetization of iron is a physical change with no new substances formed.
5. An example of a storage pest is
Solution: Weevils commonly infest and damage stored grains.
6. The solid component found on the filter paper and the liquid component that flows into a container during filtration are respectively called
Solution: The solid is the residue; the liquid that passes through is the filtrate.
7. A capacitor is connected in a series circuit with LED, a battery and a switch. When the circuit is closed, the LED
Solution: The LED flashes briefly as the capacitor charges, then goes off.
8. The ion that causes hardness in water is
Solution: Magnesium ions (Mg²⁺) contribute to water hardness.
9. Which of the following substances are matter?
I. Hydrogen
II. Air
III. StoneSolution: All listed examples—hydrogen gas, air, and stone—are forms of matter.
10. The main reason for staking tomato is to ensure
Solution: Staking supports the plant, promoting upright growth and easier harvesting.
11. Which of the following statements about clayey soil is not true? It
Solution: Clayey soil actually swells when wet and shrinks when dry.
12. It is not advisable to use old electrical gadgets because they
Solution: Old or worn electrical devices can pose safety hazards and become dangerous.
13. Which of the following planets are closer to the sun than the Earth?
Solution: Mercury and Venus both orbit closer to the Sun than Earth.
14. Which of the following statements about pressure in liquids is/are correct?
I. Pressure in liquids at the same level acts equally in all directions.
II. Pressure in liquids depend on the area of the liquid.
III. Pressure in liquids decreases with depth.Solution: Pressure at the same depth is equal in all directions; it increases with depth.
15. Soil depletion is not caused by
Solution: Afforestation (planting trees) helps prevent soil depletion.
16. What force makes a ripe mango to fall from a tree?
Solution: Gravity pulls the mango downward when it detaches from the stem.
17. Urea is a good source of
Solution: Urea is widely used as a nitrogen fertilizer.
18. Which of the following statements are reasons for conserving energy?
I. Insufficient production of energy
II. Increasing demand of energy
III. Limiting production of carbon (IV) oxideSolution: Energy conservation addresses supply limits, rising demand, and reduces CO₂ emissions.
19. A force meter measures
Solution: A force meter (spring scale) measures weight (force due to gravity).
20. Which of the following bodies are natural sources of light?
I. Moon
II. Sun
III. Glow WormSolution: The Sun and glow worms emit their own light; the Moon reflects sunlight.
21. Which of the following characteristics is/are of the image formed in a pinhole camera? The image is
I. inverted.
II. virtual.
III. diminished.Solution: Pinhole camera images are real, inverted, and smaller than the object.
22. The floor of a room has length 20 m and breadth 15 m. Determine the area of the floor.
Solution: Area = length × breadth = 20 m × 15 m = 300 m².
23. Rainfall is as a result of
Solution: Low-pressure systems cause air to rise and condense into rain.
24. An example of a first class lever is
Solution: A crow bar is a first-class lever with the fulcrum between effort and load.
25. Green plants have the ability to make their own food hence they are known as
Solution: Producers synthesize their own food via photosynthesis.
26. The periodic table is an arrangement of elements according to increasing
Solution: Modern periodic law orders elements by increasing atomic number.
27. The number required to make the following chemical equation balanced is: H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
Solution: Balanced: 2 H₂ + O₂ → 2 H₂O, coefficient for H₂ is 2.
28. The ovary, style and stigma are collectively known as the
Solution: The pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower.
29. A mixture of alcohol and water can best be separated by
Solution: Distillation separates liquids based on different boiling points.
30. An atom forms bond by losing one electron, the charge on the ion formed is
Solution: Losing one electron leaves the ion with a +1 charge.
31. The hard outer surface of a tooth is called
Solution: Enamel is the hardest, outermost layer of a tooth.
32. People who travel in space are called
Solution: Astronauts are trained to travel and work in space.
33. The practice of growing cowpea and maize on a piece of land at the same time is known as
Solution: Mixed cropping involves growing two or more crops simultaneously.
34. A lunar eclipse may occur when the
Solution: During a lunar eclipse, Earth is between the Sun and Moon.
35. Which of the following instruments can be used to measure the diameter of a circle?
Solution: A metre-rule can measure the straight-line distance across a circle.
36. When gases are heated they
Solution: Heating increases kinetic energy, reducing intermolecular attractions.
37. The shoot system of a flowering plant develops from the
Solution: The plumule develops into the shoot system of a plant.
38. The diagram below is an illustration of a transistor. The arrow shows the direction of:
Solution: The arrow in a transistor symbol indicates the direction of hole flow.
39. Digestion of protein begins in the stomach and ends in the
Solution: Protein digestion continues in the small intestine via enzymes.
40. Which of the following substances is a compound?
Solution: Sucrose is a chemical compound made of glucose and fructose.
SECTION B
Answer All Of Question 1
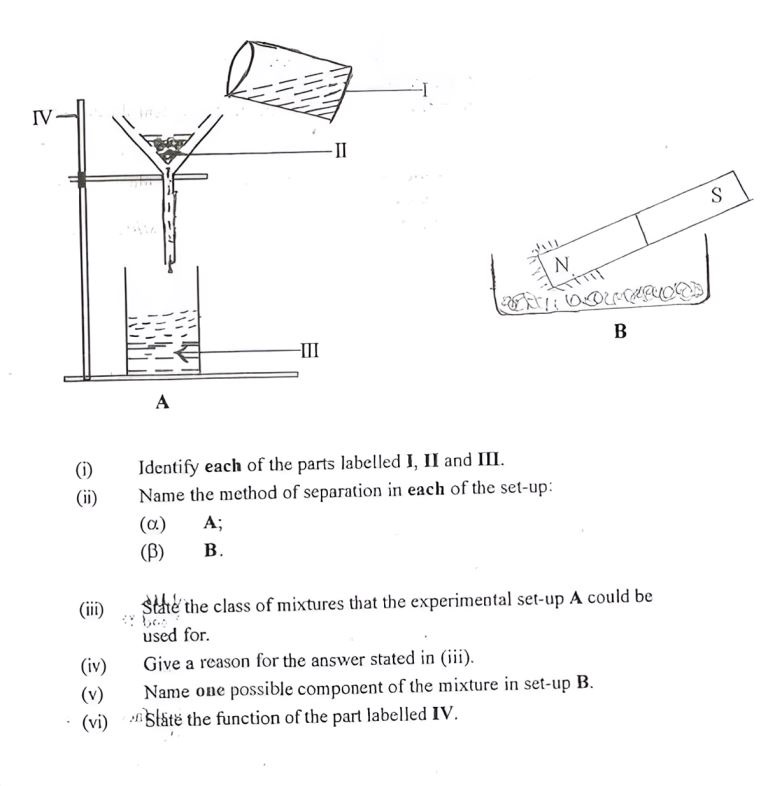
1.0. (a) The diagrams below are illustrations of an experiment set-up. study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
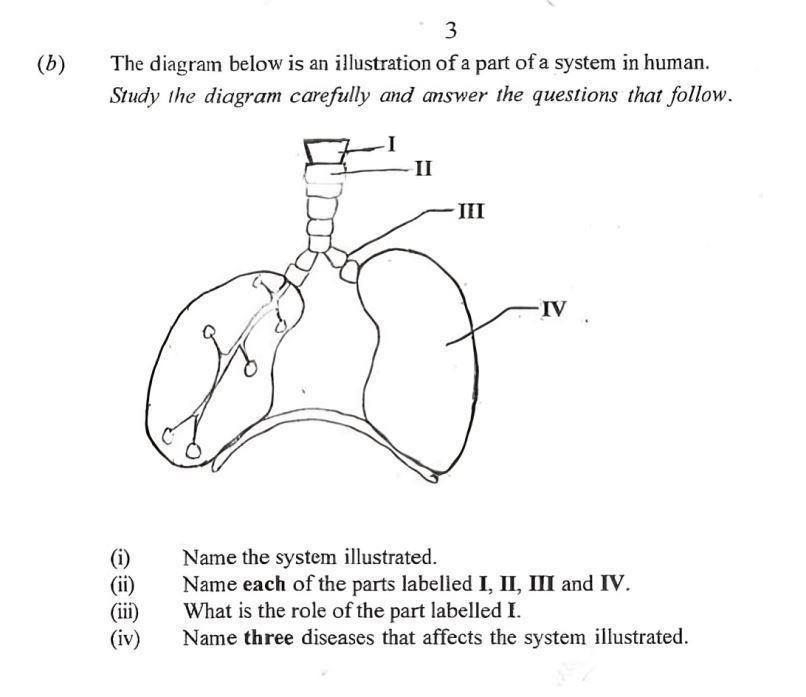
(b) The diagram below is an illustration of a part of a system in human. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
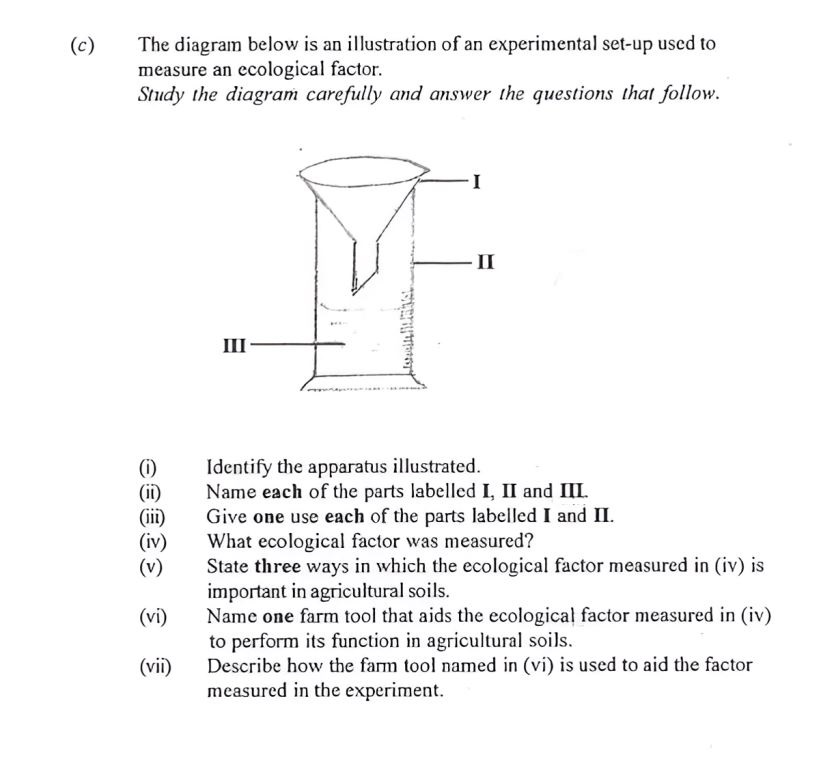
(c) The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up used to measure an ecological factor. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
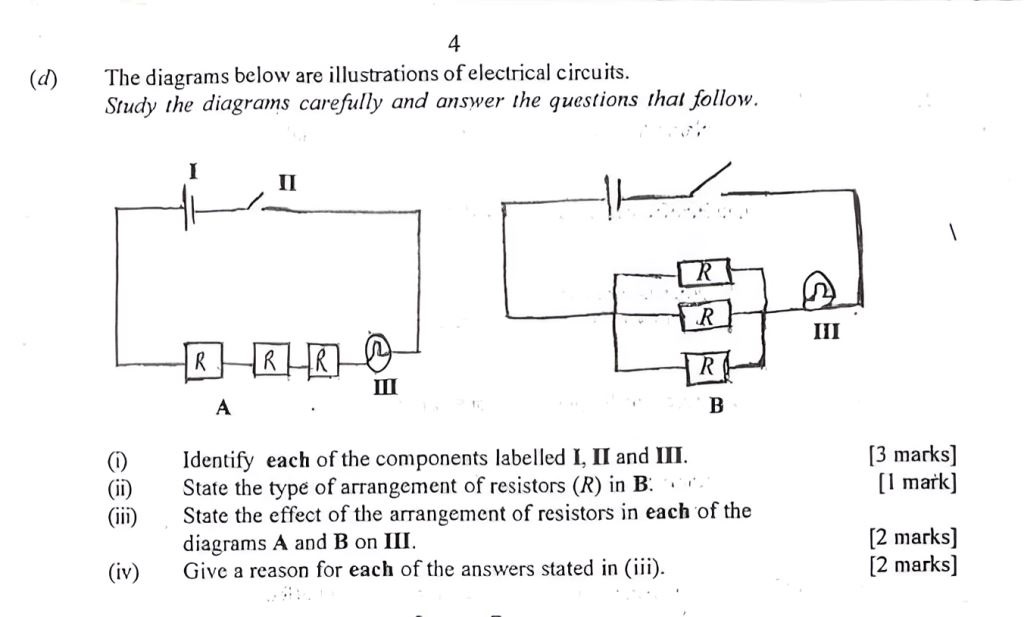
(d) The diagrams below are illustrations of electrical circuits. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Solution:
(i) I: Beaker
II: Filter paper (in a funnel)
III: Filtrate
(ii)
(iii) Filtration
(ii) (α) A: Filtration
(β) B: Magnetic separation / magnetization
(iii) Solid - liquid mixture
(iv) Experimental set-up A is used for separating an insoluble solid from a liquid
(v) Iron filings, Powedered chalk
(vi) It holds the setup in possition
(i) Respiratory system
(ii) I: Larynx
II: Trachea
III: Bronchus (or Bronchi)
IV: Lung
(iii) The larynx (voice box) is responsible for producing sound (voice).
(iv) Asthma, Pneumonia, Tuberculosis (Any three from common respiratory diseases)
(i) Rain gauge
(ii) I: Funnel
II: Measuring cylinder
III: Outer casing/collector
(iii) I (Funnel): To collect and direct rainwater into the measuring cylinder.
II (Measuring cylinder): To measure the volume of collected rainwater.
(iv) Rainfall
(v) Provides water for plant growth; Aids in dissolving nutrients in the soil for plant uptake; Helps in the weathering of rocks to form soil; Washes away accumulated salts; Leaching of nutrients (Any three)
(vi) Plow/Plough
(vii) A plow/plough is used to till or turn over the soil. This loosens the soil, improving infiltration and percolation of rainwater, making it more available for plant roots.
(i) I: Cell/Battery
II: Switch
III: Bulb/Lamp
(ii) A: Series
B: Parallel
(iii) A: The bulb (III) will be dimmer.
B: The bulb (III) will be brighter.
(iv) A: In a series arrangement, the total resistance increases, reducing the current flowing through the bulb, thus making it dimmer.
B: In a parallel arrangement, the total resistance decreases, increasing the current flowing through the bulb, thus making it brighter.
2.0. (a) State three differences between metals and non-metals in terms of their physical properties.
(b) (i). Explain the term active region as applied to transistors
(b) (ii). State what happens in the active region of a transistor
(c) (i). State two effects of lack of protein in the diet of humans
(c) (ii). Describe briefly the chemical test for glucose
(d) (i). What are soil resources?
(d) (ii). Describe briefly the chemical test for glucose


Solution:
(a) Solution: Metals
Mostly solid (except mercury)
Lustrous (shiny)
Malleable
Ductile
Good conductors of heat and electricity
High density
High milting or boiling point
Non Metals
Solid, liquid, or gas
Dull (except graphite, iodine)
Brittle
Non-ductile
Poor conductors (except graphite)
Low density
Low
(i) The active region in a transistor is the operating mode where the transistor acts as an amplifier. In this region, the transistor is forward-biased at the base-emitter junction and reverse-biased at the base-collector junction.
(ii) In the active region, a small change in the base current controls a large change in the collector current. This property allows the transistor to amplify electrical signals.
(i) Kwashiorkor, Marasmus, stunted growth, poor wound healing, weakened immune system, edema. (Any two)
(ii) Add Benedict's solution to the sample and heat the mixture in a water bath. If glucose is present, the blue Benedict's solution will change color through green, yellow, orange, to a brick-red precipitate.
(i) Soil resources refer to the components of the soil that are valuable and can be used by humans, particularly for agriculture and supporting ecosystems. This includes the minerals, organic matter, water, and air within the soil.
(ii) Continuous cropping without replenishment, overgrazing, deforestation, bush burning, excessive tillage, monoculture, improper use of fertilizers. (Any two)
3.0. (a) List in the correct order, the organs through which food passes from the mouth to the anus.
(b) State the components of a balanced ration for feeding poultry.
Solution:
(a) Solution: Mouth -> Oesophagus -> Stomach -> Small Intestine -> Large Intestine -> Anus
(b) Solution: A balanced ration for poultry should contain carbohydrates (energy), proteins (growth and repair), fats (energy and vitamins), vitamins (various metabolic functions), minerals (bone formation, eggshell formation, etc.), and water.
(i) When magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed. Equation: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) -> MgCl₂(aq) + H₂(g)
(ii) When potassium reacts with water, potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas are formed. The reaction is vigorous and produces heat, which can ignite the hydrogen gas. Equation: 2K(s) + 2H₂O(l) -> 2KOH(aq) + H₂(g)
(i) Increase in temperature, change of state (melting, boiling, sublimation), thermal expansion, chemical change (decomposition, reaction). (Any two)
(ii) The purple color of the potassium permanganate crystals will spread throughout the water.
(ii)(α)
(ii)(β) Diffusion
4.0. (a)
(b) Explain briefly why air is regarded as a mixture.
(d) Give four reasons for planting crops in rows.
Solution:
(i) Egg, Larva, Pupa, Adult
(ii) Pupa
(b) Solution: Air is regarded as a mixture because it is composed of different gases (like nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, etc.) that are not chemically bonded together and can be separated by physical means.
(i) A magnetic pole is one of the two regions in a magnet where the magnetic field is strongest. These are called the North pole and the South pole.
(ii) In electric bells, in relays, in loudspeakers, in lifting heavy magnetic materials (electromagnets), in doorbells. (Any two uses of temporary magnets, often electromagnets)
(d) Solution: Allows for easy weeding, facilitates pest and disease control, enables efficient irrigation and fertilizer application, makes harvesting easier, allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, helps in calculating plant density. (Any four)
5.0. (a)
(b) State three reasons why sandy soil cannot support effective plant growth.
Solution:
(i) Calcium and Phosphorus
(ii) Dental caries (tooth decay), Periodontal disease (gum disease), Gingivitis. (Any two)
(b) Solution: Poor water retention capacity, low nutrient content, poor cation exchange capacity, easily eroded, high infiltration rate leading to leaching of nutrients. (Any three)
(i) Drawing of an atom with a nucleus containing 13 protons (+) and 14 neutrons (n). Electron shells around the nucleus with electrons arranged as 2, 8, 3. Labels for nucleus, protons, neutrons, electrons, and shells. (Visual representation required, but described here).
(ii) The atom has 3 valence electrons in its outermost shell. Its valency is 3.
(i) Hydraulic brakes in vehicles, hydraulic lifts, syringes, artesian wells, siphons, pressure cookers, liquid in a U-tube manometer. (Any three involving fluid pressure)
(ii) Plastic, rubber, wood, glass, ceramic, air. (Any one)
6.0. (a) Explain the term mixed cropping.
Solution:
(a) Solution: Mixed cropping is the practice of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land.
(i) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal, in a fixed proportion.
(ii) Copper and Zinc
(i) Water pollution, harm to aquatic life, spread of waterborne diseases, unpleasant odor, eutrophication, reduction in the availability of clean water. (Any three)
(ii) Chlorophyll absorbs light energy (primarily red and blue wavelengths) from the sun, which is essential for photosynthesis.
(ii)(α)
(ii)(β) Water is a reactant in photosynthesis; it is split during the light-dependent reactions (photolysis) to provide electrons and protons, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. It also helps transport nutrients in the plant.
(i) In physics, work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied over a distance, and the force has a component in the direction of displacement. It is calculated as the product of the force and the distance moved in the direction of the force.
(ii) Work done = Force × Distance Work done = 20 N × 3.2 m Work done = 64 Joules